A telescope tasked with making the largest-ever map of the universe has confirmed a harsh, if unsurprising, truth: Nothing lasts forever — not cold November rain, or even the cosmos itself.
Using a vast catalog of observations from the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Euclid and Herschel space telescopes, a team of 175 researchers has taken the most comprehensive reading of the universe’s temperature ever recorded. By studying the heat emitted by stardust in more than 2 million galaxies, the team found that galaxies have grown slightly cooler and seen star formation rates slow down over the past 10 billion years of cosmic history.
According to the researchers, these small-but-clear downward trends hint that the universe’s peak days of growth are over. While the expiration date for the cosmos is still a mind-bogglingly long time away (somewhere between 33 billion and 1 quinvigintillion years — that’s 1 followed by 78 zeros — by recent estimates), the new findings suggest that, in terms of star formation rates, it’s all downhill from here.
A 3D map of the universe
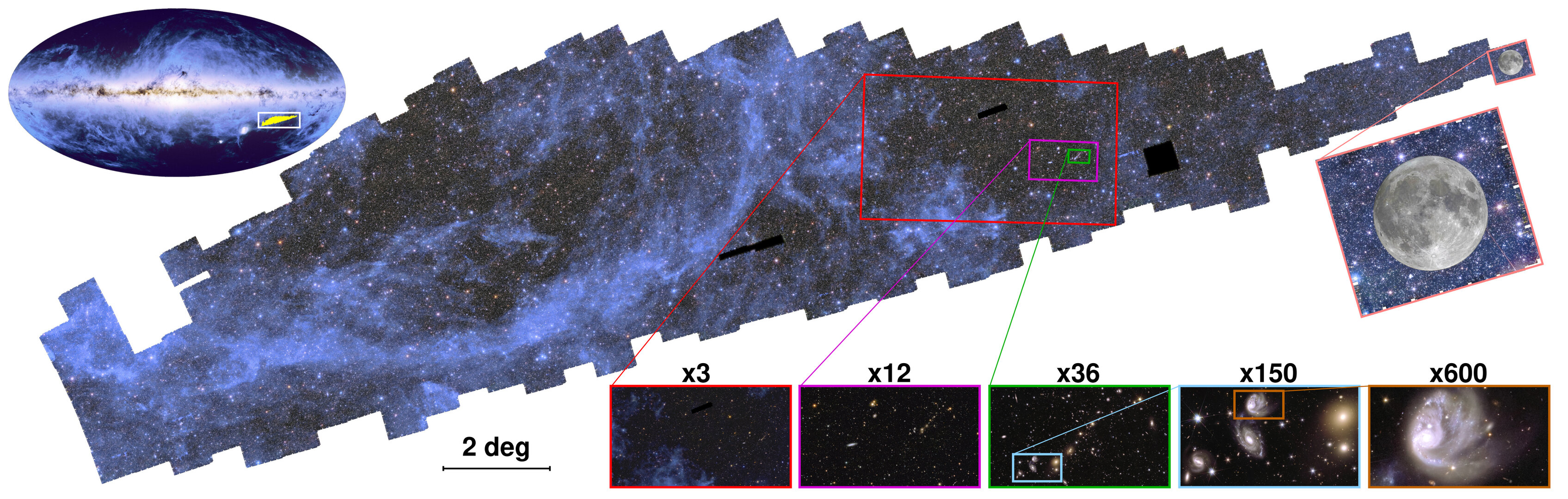
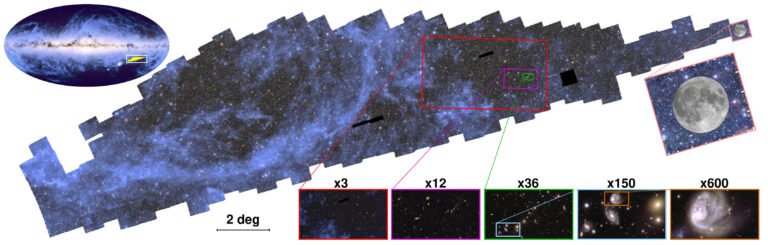
In March, ESA’s recently activated Euclid telescope shared its first major data release, including observations of 26 million galaxies stretching more than 10.5 billion light-years into the cosmic distance. This was just the first phase of the telescope’s mission to build the largest-ever 3D map of the universe, with the ultimate goal of charting about 1.5 billion galaxies covering one-third of the night sky.
For their new study, the researchers looked at 2.6 million galaxies cataloged in Euclid’s first data release and combined them with archival observations from ESA’s Herschel Space Observatory, which was active from 2009 to 2013). While Euclid’s pair of onboard instruments are tuned to record visible and near-infrared light, Herschel’s instruments detected far-infrared light. Therefore, combining these data sets allowed the team to study the heat emitted by stardust across a wide range of wavelengths, offering the most comprehensive measurements of galactic temperatures ever taken.
“By combining the data and having such a huge sample of galaxies … we can produce the most statistically robust calculations to date,” lead study author Ryley Hill, a postdoctoral research fellow at UBC, said in the statement.
The team found that the average temperature of galaxies has cooled only slightly over the past 10 billion years, falling by just 10 kelvins. While stars like the sun blaze at more than a million kelvins, galaxies are mostly made of empty space, meaning their average temperatures are far lower. The average galactic temperature of the earliest galaxies observed in the new survey was about 35 K (minus 396 F, or minus 238 C), the researchers found.
It’s a small change, but the heat of stardust directly correlates to star formation, the team noted. Hotter galaxies tend to have higher rates of star formation because they contain a greater number of hot, massive stars. By the same token, galaxies with less star formation tend to be cooler, on average. The team’s research further confirms this correlation and proves that star formation is slowly waning across the cosmos.
Dust to dust
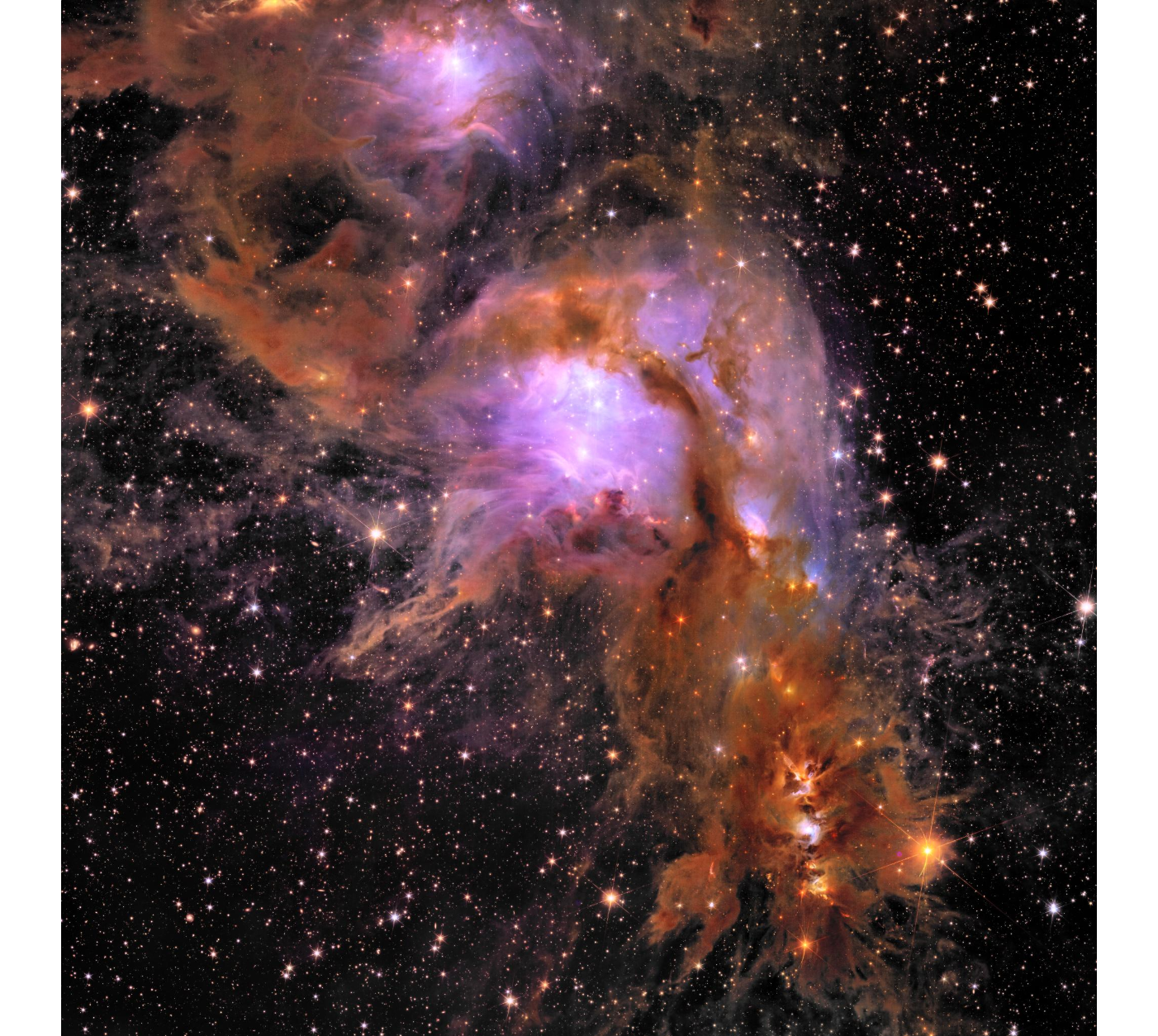

It may be a chore to deal with on Earth, but dust is crucial to the life cycle of stars. Stars form when clouds of gas and dust become so dense that they collapse under their own gravity, heating up and spinning in the process. If one of these collapsed clumps becomes hot and dense enough, nuclear fusion triggers in its core, forming a star. Eventually, when the star exhausts its supply of nuclear fuel billions of years later, it will explode in a supernova, spewing yet more dust into its neighborhood and allowing the next generation of stars to grow.
Galaxies can run out of star-forming material in a number of ways; they can be cut off from their gas supply during galaxy mergers, or see their star-forming matter violently expelled into space by supermassive black hole outbursts, to name a few. Eventually, a galaxy without sufficient star-forming material becomes quenched — starved of fuel, and doomed to smolder out.
The new results hint that our universe is well on its way to being totally quenched — but, again, not for an unfathomably long time. Earth’s sun will exhaust its fuel and explode long before the Milky Way galaxy runs dry, and more massive objects like black holes will live on for many eons after that. In the meantime, the new research offers the most precise probe yet of some of the key conditions of galaxies throughout the universe — measurements that will be essential in Euclid’s quest to build the ultimate map of our cosmos.